Hypervisor Stack
This section provides an in-depth look at the Labo-CBZ virtualization infrastructure's cornerstone: the hypervisor stack. This stack is pivotal in Labo-CBZ's virtualization ecosystem, facilitating the streamlined management and deployment of virtual machines (VMs).

Overwiew
Hypervisor Technology
At the heart of Labo-CBZ's virtualization strategy is Proxmox, a leading hypervisor platform. Proxmox delivers a comprehensive suite for virtualization management, encompassing VM creation, management, and seamless migration across the infrastructure. Its user-friendly web interface and advanced clustering features position Proxmox as the optimal solution for Labo-CBZ's evolving needs.
Cluster Configuration
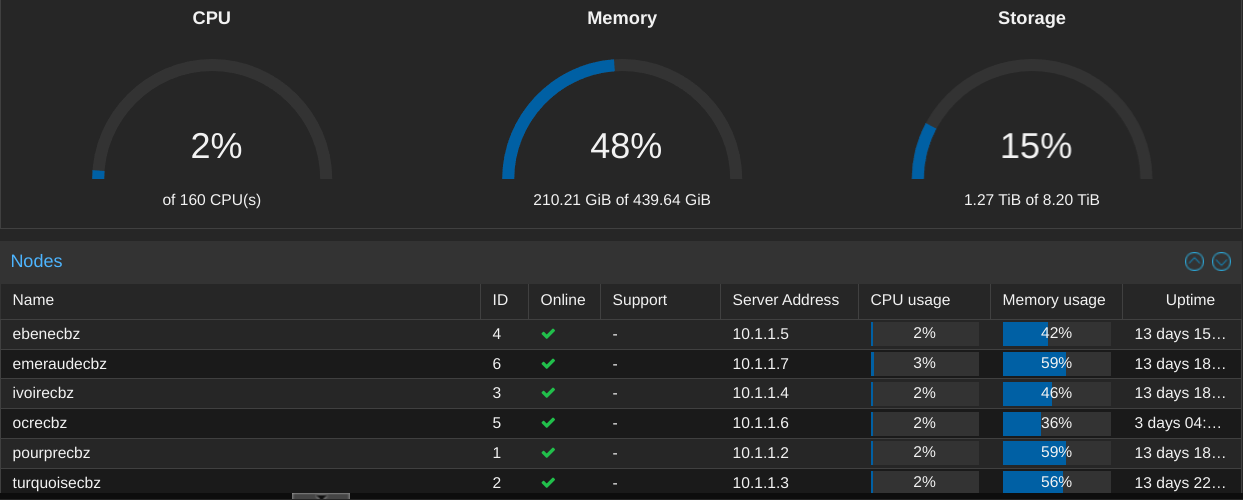
The hypervisor stack at Labo-CBZ is structured into a cluster comprising six nodes. This configuration enhances high availability and facilitates resource pooling, which, in turn, supports smooth failover and load balancing. Such a setup guarantees superior performance and reliability for critical applications.
Virtual Machine Management
Labo-CBZ employs a sophisticated approach to virtual machine (VM) management, leveraging Proxmox's robust capabilities. This includes the provisioning, monitoring, and maintenance of VMs, ensuring optimal performance and security. The platform's intuitive interface allows for easy VM management, while advanced features like snapshot and backup functionalities ensure data integrity and quick recovery in case of failure.
Hardware Resources
The Labo-CBZ hypervisor stack is powered by high-performance servers, each equipped with state-of-the-art processors and ample memory to handle intensive workloads. These servers are interconnected through a high-speed network fabric, ensuring low latency and high throughput. Storage is managed via a Ceph cluster, providing scalable and redundant storage solutions that guarantee data availability and integrity.
Physical organization
Before delving into the specifics of Labo-CBZ's physical organization, let's first take a look at the wired network diagram. This diagram provides a visual representation of how nodes, including servers, switches, routers, and other networking equipment, are interconnected within the infrastructure.

The wired network diagram acts as a foundational guide for comprehending the physical configuration of Labo-CBZ's infrastructure. This diagram delineates the interconnections among diverse components, emphasizing the routes data traverses throughout the network.
Dual-NIC Configuration for VMs/LXCs Networking
Labo-CBZ enhances network reliability and performance for Virtual Machines (VMs) and Linux Containers (LXCs) through a dual-NIC configuration. This setup ensures network redundancy, providing a failover mechanism that maintains network connectivity even if one NIC fails. It also facilitates load balancing, distributing network traffic across two interfaces to optimize bandwidth utilization and reduce bottlenecks.
VLAN-Aware Switch Integration for Network Segmentation
Network segmentation at Labo-CBZ is achieved through the integration of VLAN-aware switches. This approach allows for the creation of isolated network segments (VLANs) within the same physical infrastructure, enhancing security by segregating traffic based on function, department, or application. It simplifies network management and improves performance by reducing broadcast traffic, thereby creating a more efficient and secure network environment.
Hypervisor Integration with Ceph Storage
Labo-CBZ leverages the power of Ceph storage, integrating it seamlessly with the hypervisor environment to provide a highly scalable and resilient storage solution. This integration allows for the efficient management of VM and LXC storage, offering features such as live migration, snapshotting, and dynamic storage provisioning. Ceph's distributed architecture ensures high availability and fault tolerance, making it an ideal choice for Labo-CBZ's storage needs.
